Copper-Catalyzed Hydroamination of Allenes: from Mechanistic Understanding to Methodology Developmen
ACS Catalysis 2017, 7 (7), 4253–4264
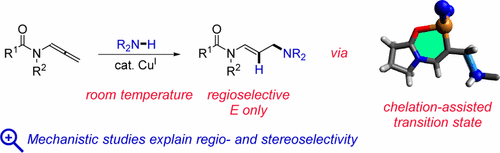
Experimental and theoretical mechanistic studies on the Cu(OTf)2-catalyzed hydroamination reaction of terminal allenes with secondary amines reveal that in situ generated cationic Cu(I) is the catalytically active species and explain the observed regio- and stereoselectivity for the unbranched E product. Insight into the structure of the relevant transition states allowed the generalization of this methodology to allenamides and N-allenylcarbamates under unprecedentedly mild and functional-group-tolerant conditions. Chelation effects by the amide oxygen in addition to electronic effects explain the high innate reactivity of this class of substrates.